It’s both an exciting and challenging time for manufacturers to bring new products to market in this era of rapid innovation. Changing customer expectations and shrinking budgets are among the challenges. Manufacturers are therefore utilizing realistic simulation to gain a competitive advantage by lessening the need for physical testing, increasing product reliability, and reducing the time to market. For realistic structural simulation, SIMULIA Unified FEA provides a comprehensive solution that covers routine and advanced workflows across various industrial applications. Among the many updated features and improvements in SIMULIA 2022 (Abaqus, Isight, TOSCA, FESAFE), there are several significant ones. Following is a summary of some of the new features:
ABAQUS 2022
Users can easily create, edit, monitor, diagnose, and visualize advanced analyses using the Abaqus/CAE Complete Abaqus Environment. Using the intuitive interface, modeling, analysis, job management, and results visualization are integrated into a consistent, easy-to-use workspace, even for new users. With Abaqus/CAE, one can interact with computer-aided engineering concepts such as feature-based, parametric modeling, interactive and scripted operations, and user interface customization. The following paragraph covers the recent updates in different categories.
Structural Mechanics
- The LaRC05 damage initiation criteria for fiber-reinforced composites are now available in Abaqus/Standard.
- The Hosford-Coulomb damage initiation criteria for ductile metals are now available in both Abaqus/Standard and Abaqus/Explicit.
- The Valanis-Landel hyper elastic material model to analyse rubber-like materials is now available in Abaqus/Standard.
- Band-limited damping in Abaqus/Explicit allows the user to apply a desired uniform damping ratio over a specified frequency range.
- Distortion control is now available for the C3D10 element in Abaqus/Explicit.
- Distributions to specify layer thicknesses for composite solid elements and use wedge (triangular prism) elements with a composite solid section definition.
Analysis Techniques
- Cyclic symmetry analysis technique can be used now in Abaqus/Explicit to reduce simulation time and memory requirement.
- Abaqus/Standard now enables running multiple nonlinear load cases within a single job. This new capability significantly reduces run time and the number of output files compared to running multiple jobs.
- The import capability has been extended to transfer nodal temperatures and user-defined field variables between Abaqus/Standard and Abaqus/Explicit.
- The extended finite element method (XFEM) now supports procedures with temperature degrees of freedom.
- Implicit dynamic analysis in Abaqus/Standard now supports adjoint sensitivities for topology, shell thickness, and lattice sizing design variables.
Modelling and Visualisation
- Abaqus/CAE now provides a tool to remove selected data from an odb which can significantly reduce file size.
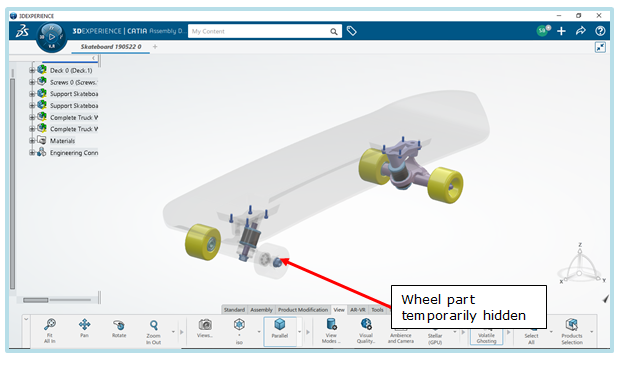
- CATIA V5 geometry can now be directly imported into the Linux platform.
- SOLIDWORKS assemblies can now be imported as multiple parts.
- User control over shear flow visualization has been improved.
- Abaqus/CAE now supports small-sliding general contact in Abaqus/Standard
- Abaqus/CAE now supports analytical fields when defining composite ply thickness distributions.
Performance and HPC
- Abaqus/Explicit can now be executed in hybrid mode using a combination of MPI and threads, with each MPI process launching a user-specified number of threads. Hybrid execution takes advantage of the Non-Uniform Memory Access (NUMA) architecture and the trend of increasing the number of cores available on each socket.
- The iterative linear equation solver in Abaqus/Standard now supports common modelling features, including hybrid elements, connector elements, distributing couplings, and hard contact.
- Parallel scaling of linear static simulations with many load cases is significantly improved.
ISIGHT 2022
ISight provides designers, engineers, and researchers with an open system for integrating design and simulation models—created with various CAD, CAE, and other software applications—to automate the execution of hundreds or thousands of simulations. ISight allows users to save time and improve their products by optimizing them against performance or cost metrics through statistical methods, such as Design of Experiments (DOE) or Design for Six Sigma. ISight combines cross-disciplinary models and applications in a simulation process flow, automates their execution, explores the resulting design space, and identifies the optimal design parameters based on required constraints. ISight’s ability to manipulate and map parametric data between process steps and automate multiple simulations significantly improves efficiency, reduces manual errors, and accelerates the evaluation of product design alternatives. Recently the 2022 release of ISight was announced, with new developments that include feature enhancements and component updates. Highlights of ISight R2022 include:
Abaqus Component Upgrade
- Isight Abaqus component creates a direct link to Abaqus, allowing automated execution of Abaqus from Isight
- In Isight 2022, the Abaqus component is enhanced to support Abaqus 6.14 through Abaqus 2022 and maintenance releases thereof
- No other functional changes to the component
- Middleware upgrade
- Apache TomEE
- Isight 2021 & previous releases shipped Apache TomEE 1.7.2
- Isight 2022 ships Apache TomEE 8.0.5
- All the security fixes delivered by TomEE between these versions are now automatically available for SEE, Webtop, and Web Dashboard applications running on TomEE
- Oracle database
- The supported version of Oracle database is upgraded to Oracle 19c
- Microsoft SQL Server database
- The supported version of the Microsoft SQL Server database is upgraded to Microsoft SQL Server 2019
- Older releases of the Oracle and Microsoft SQL Server are not supported
- Support for the Oracle WebLogic application server has is removed
- Customers who were using Oracle WebLogic application server would need to migrate to IBM WebSphere or Apache TomEE application server
- Isight/SEE 2022 Improved Stability and Reliability
FESAFE 2022
There are certain updates introduced in FE Safe 2022. Some are the enhancement are listed below: –
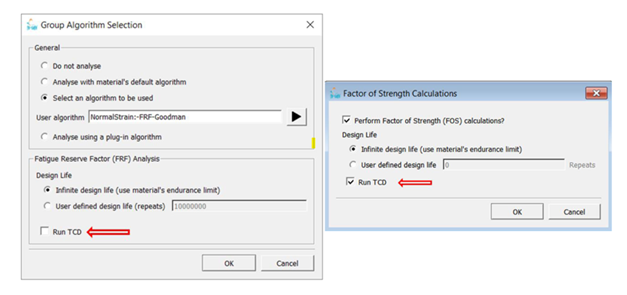
FE-SAFE: TCD (THEORY OF CRITICAL DISTANCES)
- A new interface in 2021 FD04
- The algorithm used at the sub-surface location for TCD calculation = algorithm chosen for the surface as shown below in the figure.
- Expanded MSC options
- New TCD and FOS tabs in Analysis Options
FE-SAFE: THERMO-MECHANICAL FATIGUE FROM ELASTIC-PLASTIC FEA
- Based on DTMF technology developed at Fraunhofer IWM over the last 20 years
- Available as a plugin for evaluation purposes to qualified users – Contact Hawla, De Morais, or Sobczak to arrange a call with the users
- fe-safe/TURBOlife, already in CA, will become deprecated
- Damage (1∕𝑁_𝑓 ) calculated per reversal and accumulated using Miner’s rule
- Reversals determined via Wang & Brown multi-axial cycle counter
- Damage (1⁄N_f ) calculated per reversal and accumulated using Miner’s rule
- Reversals determined via Wang & Brown multi-axial cycle counter
|
FE-SAFE: GENERAL 2021 ENHANCEMENTS |
FE-SAFE: GENERAL 2022 ENHANCEMENTS |
|
|
TOSCA 2022
Below are few of the recent updates incorporated in TOSCA 2022:
Usability
- Unified Interpolation scheme for Topology optimization
Rib Design manufacturing constraint for Topology Optimization
- More robust method to restrict the maximum member size in optimized structures.
- It prevents floating material to a large degree and only affects the result if the thickness is violated.
- NEW: Enforce manufacturing constraints in bead sensitivity optimization. It can improve the manufacturability of the final result.
Improved Maximum Member Constraint for Topology Optimization
- This feature allows the user to create responses based on abaqus user subroutines, as shown below.
- The user can create stress based or plasticity based responses.
- Multiple responses can be used in a single optimization.
- Examples : laminate failure criteria, plastic strain responses etc.

Manufacturing Constraints for Bead Sensitivity Optimization
- This allows a user to continue an optimization that has ended prematurely
- The user can change the maximum number of design cycles
- The modification of convergence settings is also allowed
- This differs from restart as all the optimization parameters calculated in the last cycle are preserved.