How an Efficient Geological Model Enhance Deposit Evaluation
- Pramod Sarangi
- December 25, 2024
How an Efficient Geological Model Enhances Deposit Evaluation
Mineral Resource estimation and classification are highly dependent on the confidence in the model of the orebody geometry, known as the geological model.
An understanding of the geology of a deposit is thus fundamental to the Mineral Resource evaluation process. The 3D geological model is a function of the structural and depositional complexity of the geology captured by drilling information, which is limited in the early stages of a project. The information effect has a significant impact in terms of the interpretation of the geology as well as the estimation of grade continuity and the resultant risk associated with the Mineral Resource estimate and classification.
Whenever, new drilling information becomes available, it is necessary to update and refine the geological model to appropriately constrain the resource estimates. The grade information is also updated, including statistics and the spatial correlation characteristics. This refinement is based on geological interpretations derived from the drillhole information that becomes available throughout the life of the mine; orebody knowledge that comes from working experience of the deposit, as well as familiarity with the software package used for modelling, is also important.
Transforming Geological Data into Reliable Models
There are many processes and technological availability to manage geological interoperation data, which is the key information for any exploration project.
Geological data is the most important aspect of any technical or financial evaluation of a mineral deposit because it is key to defining the location, geometric shape, and grade of the orebody.
This is why the mining organization invest lot of amount every year to collect new geoscience data, which is invaluable for making fresh interpretations and keeping mine models updated, and to manage, interrogate, and curate older data that can increase in value over time as new analytical technologies and interpretation methods become available.
But just collecting comprehensive geological datasets is not enough. Once you have them, you must be able to generate accurate, reliable geological models of the subsurface. GEOVIA solutions help you visualize the geology of your site better than ever before, and test your hypothesis above ground to ensure the best possible below-ground decisions. Effective geological data management drives operational excellence.
Transforming Geological Data into Actionable Insights with 3D Models
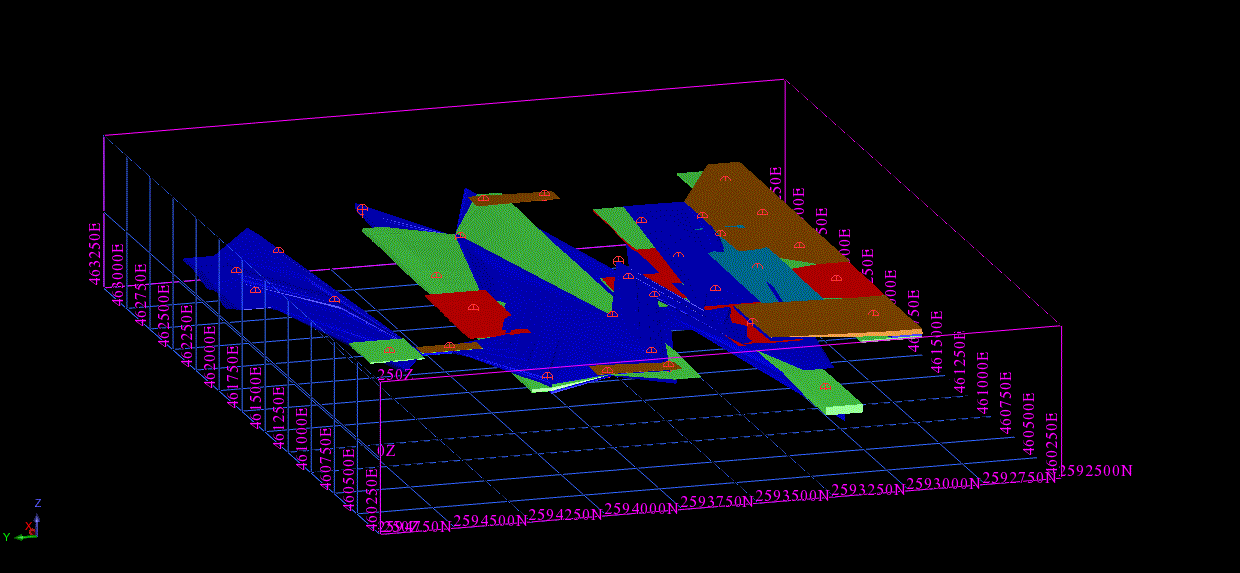
A 3D geological model is a comprehensive representation of subsurface geological structures and characteristics in a three-dimensional digital format. It integrates geological data, including drill hole information, geophysical surveys, and rock properties, to create a visual and interactive model of the Earth’s subsurface.
This model enables geologists, miners, and exploration professionals to better understand the distribution of mineral resources, geological features, and potential risks beneath the Earth’s surface. It plays a crucial role in guiding mining operations, resource estimation, environmental assessment, and decision-making processes in industries like mining, oil and gas, and environmental geology.
Geological Modeling, a Critical Process in Mining and Exploration, Typically Involves the Following Steps:
- Data Collection and Analysis: Gathering a wide range of geological data such as drill hole logs, geophysical survey data, and geochemical analyses. This data is then analyzed to understand the geological characteristics of the area.
- Interpretation and Correlation: Interpreting the collected data to identify geological structures like faults, folds, and mineralized zones. This involves correlating data from different sources to create a coherent geological story.
- Model Construction: Using specialized software, such as GEOVIA, to construct a three-dimensional model of the geology. This model integrates all the interpreted data, representing the subsurface geology in a visual and interactive format.
- Validation and Refinement: Continuously validating and refining the model as new data becomes available. This iterative process ensures the geological model remains accurate and up-to-date, reflecting any changes or new findings in the geological understanding of the area.

- Pramod Sarangi
- December 25, 2024
How an Efficient Geological Model Enhance Deposit Evaluation
How an Efficient Geological Model Enhances Deposit Evaluation
Mineral Resource estimation and classification are highly dependent on the confidence in the model of the orebody geometry, known as the geological model.
An understanding of the geology of a deposit is thus fundamental to the Mineral Resource evaluation process. The 3D geological model is a function of the structural and depositional complexity of the geology captured by drilling information, which is limited in the early stages of a project. The information effect has a significant impact in terms of the interpretation of the geology as well as the estimation of grade continuity and the resultant risk associated with the Mineral Resource estimate and classification.
Whenever, new drilling information becomes available, it is necessary to update and refine the geological model to appropriately constrain the resource estimates. The grade information is also updated, including statistics and the spatial correlation characteristics. This refinement is based on geological interpretations derived from the drillhole information that becomes available throughout the life of the mine; orebody knowledge that comes from working experience of the deposit, as well as familiarity with the software package used for modelling, is also important.
Transforming Geological Data into Reliable Models
There are many processes and technological availability to manage geological interoperation data, which is the key information for any exploration project.
Geological data is the most important aspect of any technical or financial evaluation of a mineral deposit because it is key to defining the location, geometric shape, and grade of the orebody.
This is why the mining organization invest lot of amount every year to collect new geoscience data, which is invaluable for making fresh interpretations and keeping mine models updated, and to manage, interrogate, and curate older data that can increase in value over time as new analytical technologies and interpretation methods become available.
But just collecting comprehensive geological datasets is not enough. Once you have them, you must be able to generate accurate, reliable geological models of the subsurface. GEOVIA solutions help you visualize the geology of your site better than ever before, and test your hypothesis above ground to ensure the best possible below-ground decisions. Effective geological data management drives operational excellence.
Transforming Geological Data into Actionable Insights with 3D Models
A 3D geological model is a comprehensive representation of subsurface geological structures and characteristics in a three-dimensional digital format. It integrates geological data, including drill hole information, geophysical surveys, and rock properties, to create a visual and interactive model of the Earth’s subsurface.
This model enables geologists, miners, and exploration professionals to better understand the distribution of mineral resources, geological features, and potential risks beneath the Earth’s surface. It plays a crucial role in guiding mining operations, resource estimation, environmental assessment, and decision-making processes in industries like mining, oil and gas, and environmental geology.
Geological Modeling, a Critical Process in Mining and Exploration, Typically Involves the Following Steps:
- Data Collection and Analysis: Gathering a wide range of geological data such as drill hole logs, geophysical survey data, and geochemical analyses. This data is then analyzed to understand the geological characteristics of the area.
- Interpretation and Correlation: Interpreting the collected data to identify geological structures like faults, folds, and mineralized zones. This involves correlating data from different sources to create a coherent geological story.
- Model Construction: Using specialized software, such as GEOVIA, to construct a three-dimensional model of the geology. This model integrates all the interpreted data, representing the subsurface geology in a visual and interactive format.
- Validation and Refinement: Continuously validating and refining the model as new data becomes available. This iterative process ensures the geological model remains accurate and up-to-date, reflecting any changes or new findings in the geological understanding of the area.