Lean Manufacturing:
The word “lean” means no excess. So lean manufacturing can be explained simply as manufacturing which involves nominal waste. Lean manufacturing is all about reducing waste, not just physical waste, but labor and time waste caused by some processes. When all of these wastes have been eliminated from the system, only then can it be said that the system is truly lean and optimized. In short, lean manufacturing involves continual efforts to decrease or eliminate waste starting from the design process to the manufacturing, distribution and towards the product support and the phases beyond. This necessitates work and the development of a lean culture within the workforce, which ultimately leads to added value both for the customer and the company.
Managing a Lean Manufacturing Plant:
The burden to deliver quality parts on schedule and at the same time to keep throughput times, residues and missing parts to a minimum is increasing in manufacturing planning. Shop floor management helps manufacturing companies achieve this goal. Companies have multiple teams which work to achieve the required level of productivity. Below is the representation of how many teams work to produce a product.
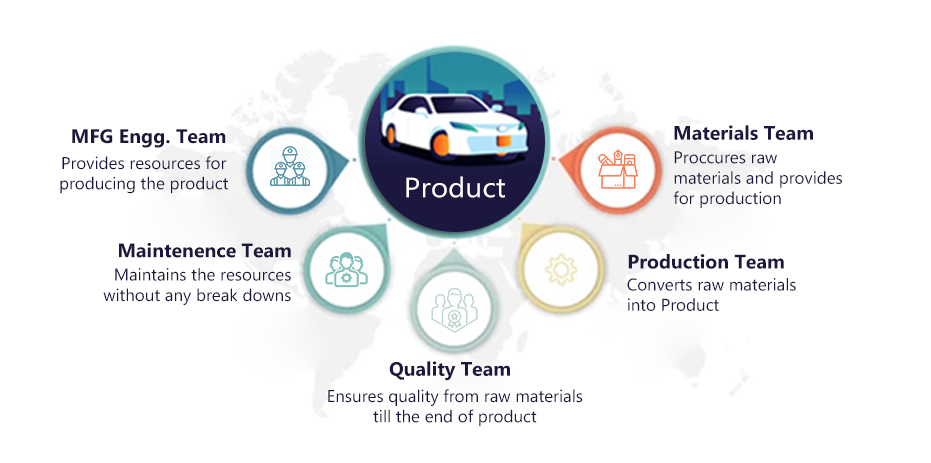
Deviating, even by any one team at any stage is not acceptable because it would affect the entire productivity of the plant.
Shop Floor Management:
Constant practice of shop floor management approaches helps to form choices, recognize deviations in productivity results and successfully solve problems. Workplace meetings are the core for creating the culture of LEAN – embedding the behavior in all operators by making it part of their work to share learnings and ideas. Also key for sustainability, part of the daily process post which managers can customize the agenda.
However, each department within the company must collect a lot of information and compile it before having the meeting. Information flow in a company for a single department is shown in the below representation.
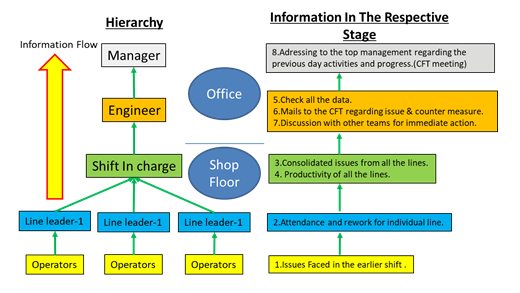
Collecting this information and compiling has to be done for easy understanding and discussion. More specifically, there are four paper practices:
(1) creating and adapting individual information spaces
(2) reinterpreting information
(3) combining information handover with social interaction
(4) visual cuing
After collecting and compiling, this information goes to the boards as shown below.

Challenges within the paper-based shop floor meeting:
- Time taken for updating the boards.
- Information transparency is missed and reviewing previous days’ issues by management is very challenging.
- No track/update of issues discussed, if they were closed or not.
- Data retrievability could be a huge issue.
Digitalize Lean Practices:
DELMIA 3DLean is a modern, customizable and interactive solution that gives managers the ability to capture, monitor, and track operational meetings on the shop floor. It enables manufacturers to bring about lean practices to make them an integral part of shop floor operations by providing critical coordination and communication capabilities. Enacting Lean practices on the shop floor help improve communication. Built on the 3DEXPERIENCE platform, DELMIA 3DLean has a widget-based web app called HIGHLIGHTS that uses touchscreen technology to deploy Lean practices to team leaders, workers, and support teams.
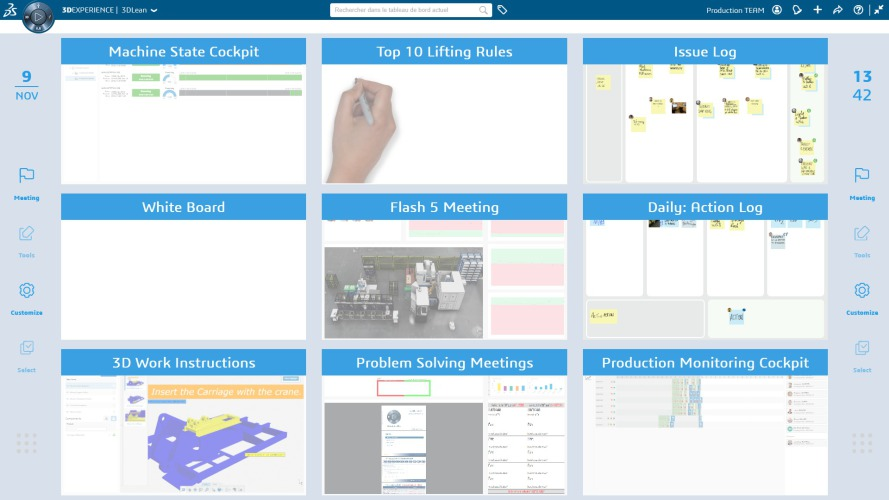
Digitalization unites shop floor data with engineers’ intellect and breaks down organizational barriers and allows each team to take the correct actions, cascade results to stakeholders, and collaborate effortlessly regardless of their role or job. It helps companies by allowing teams to add human intelligence to shop floor data when addressing operational needs. It also animates Lean work place meetings with graphically presented functions for immediate action and follow through.
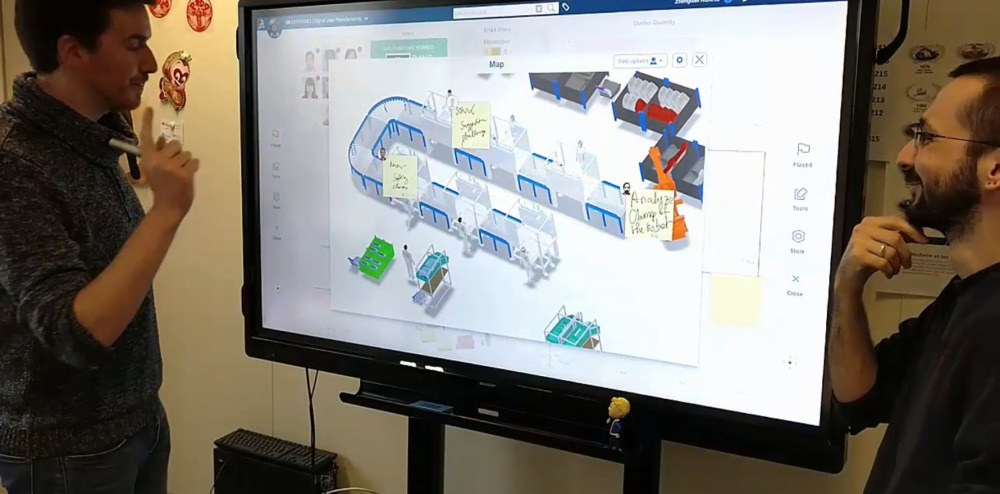
It also helps to track the discussed points. Each issue can be assigned in the board and status of the work can be checked and followed up with the responsible person for the details and solve the issues without any waste of time.
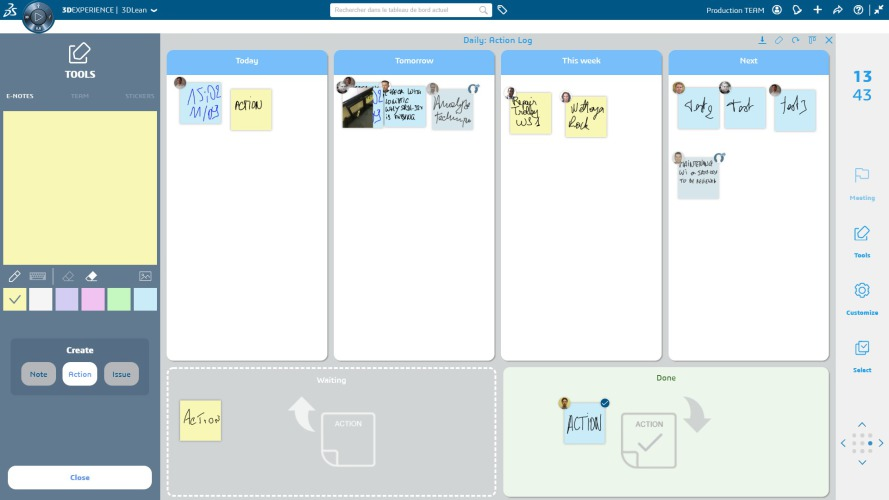
DELMIA 3DLean makes ‘Lean thinking’ a standard part of business, teams and culture by:
- Allowing flexibility to adapt to new team scenarios and context.
- Putting lean principles into action to handle operational waste, variability and efficiency.
