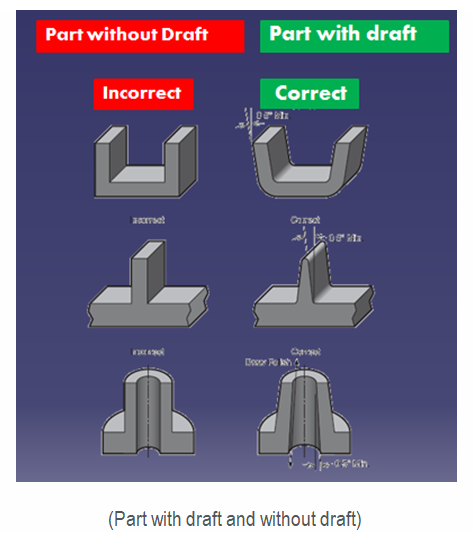
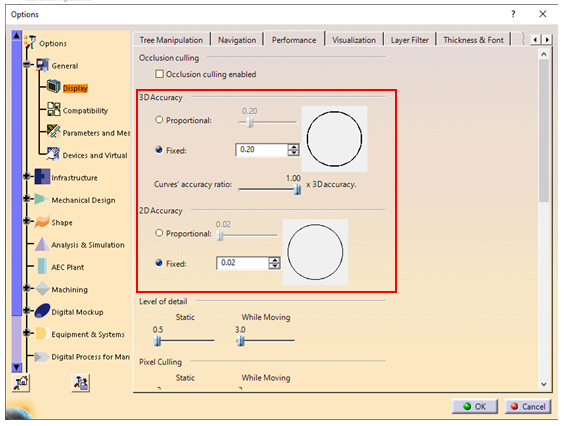
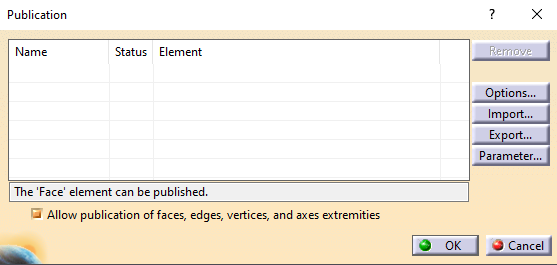
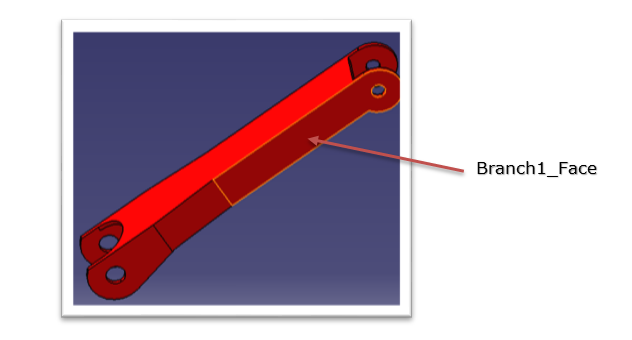
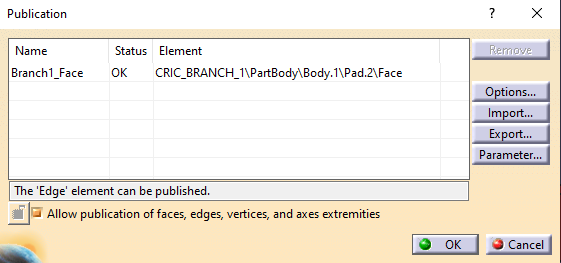
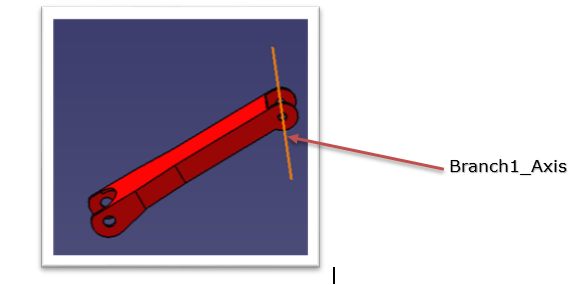
Boolean operation is an important feature in CATIA V5. Types of Boolean operations include Assemble, Add, Remove, Intersect, Union Trim, and Remove Lump.
Assemble
The Assemble command basically works considering the polarity of the solid bodies. One may be interested to know what actually is the polarity of a body. In simple words, it can be said that whenever a new body is created using material formation like pad, shaft and rib or multi-section solid, then that body can be considered as positive polar body. Pocket, groove, slot and remove multi-section solid is considered as negative polar body.
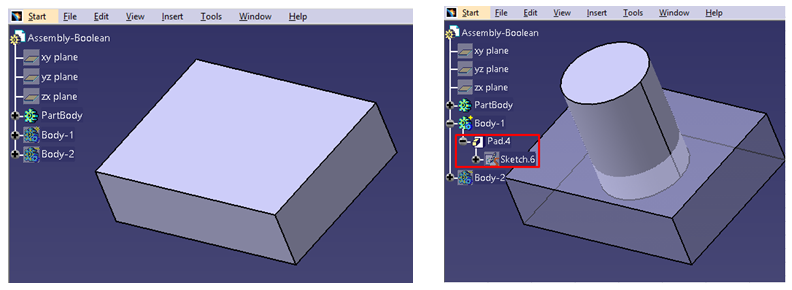
A part body is created as a rectangular block and Body-1 as a solid cylinder as shown below. Consider this Body-1 as positive polar body as it is created using pad command and intersects with part body. Now if we use Assemble Boolean operation, then this cylinder will join the rectangular part body and will act as a single body.
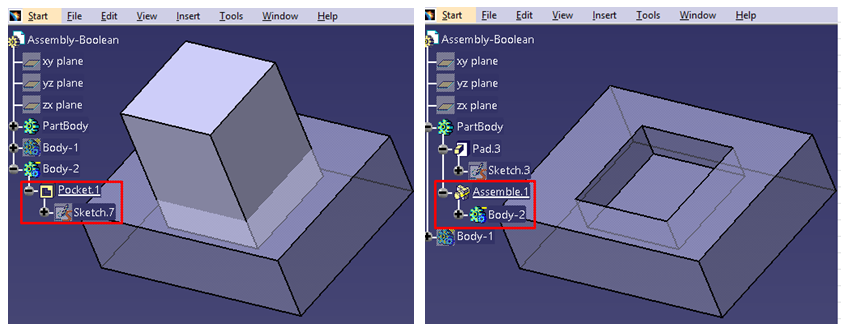
Now again Body-2 is being created as a rectangular block and is considered as negative polar body because pocket command is used. Whenever Body-2 is assembled with rectangular part body, it will go for material removal in intersected area due to the selection of negative polar body.
Add
Add operation removes only the intersected portion between two bodies so that both parts act as a single body irrespective of the polarity of the bodies. Here, the bodies may be with positive polarity or negative polarity or a combination of both.
Remove
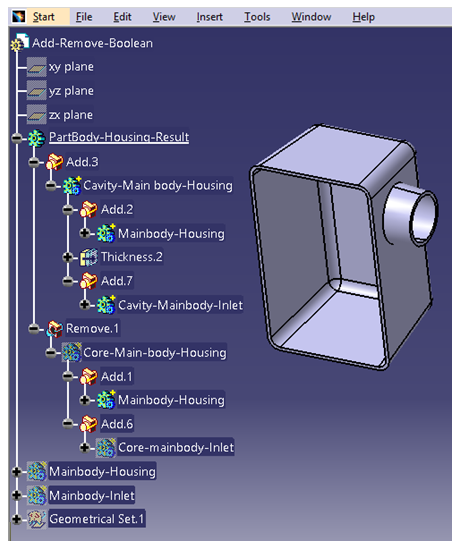
Remove operation removes the selected body first and then is merged with the second body irrespective of the polarity of the bodies. Below is an example on how to create Housing using Add and Remove Boolean operation.
Intersect
To derive a single body from two different bodies, Intersect Boolean operation is used. Basically, the intersected portion is the output which is displayed as a single body. There is no effect of polar bodies here.
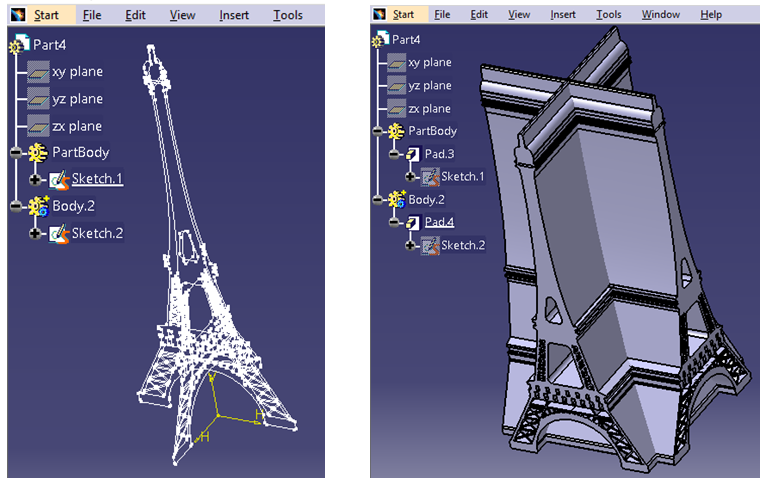
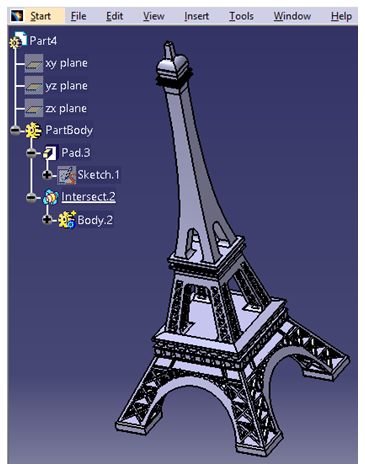
In the above example, there are two sketches intersecting each other in the first picture. In the second picture, pad is created on both sides with a certain limit. After using Intersect Boolean operation, the result shows only the common portion which can be seen in third picture.
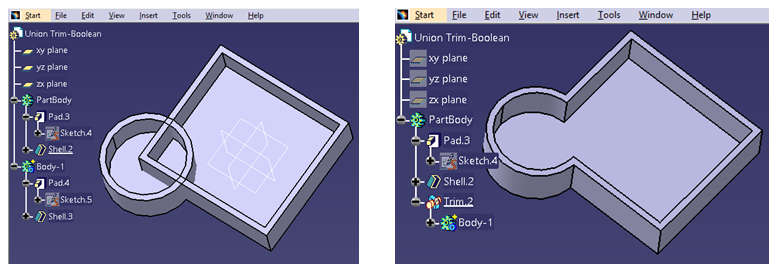
Union Trim
Unwanted material can be removed from any two bodies by using Union Trim operation which results in a single desired body.
Consider the example below:
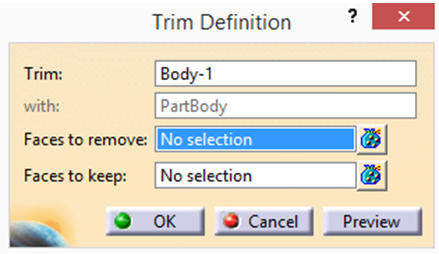
In Model Tree, it can be seen that one rectangular body is intersecting with another circular body and the unwanted intersected area needs to be trimmed. After clicking on Union Trim, it gives an option to the user to keep/remove any face. After selecting the shape to be removed, the result can be seen as below:
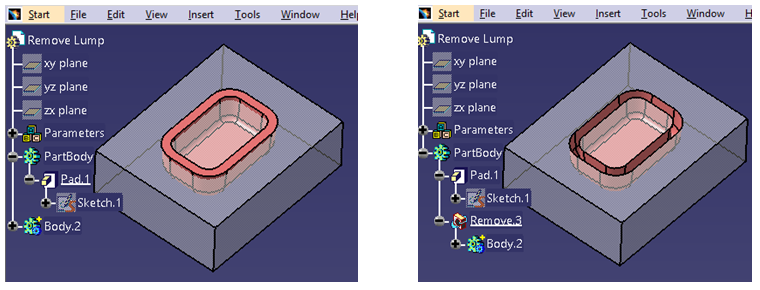
Remove Lump
Remove Lump Boolean operation removes the lump inside the body.
During the operation, a tab will give the option to the user to keep/remove any face as required. Using this Boolean operation, a user can remove N number of lump face areas.
Below is an example of creating a lump first by using Remove Boolean operation and then using Remove Lump Boolean operation, it is shown how a lump can be removed.
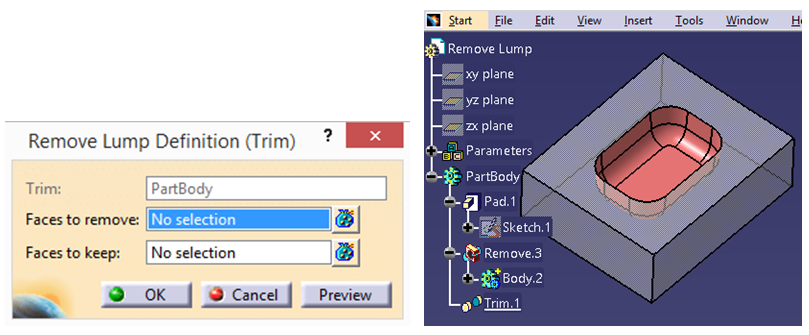
The image below shows Remove Lump definition tab which allows to choose the particular faces. After selecting the face, result is generated.
For a stable design where design features are interlinked, Boolean operation may be a good operation to go with. After all, design aspect is important as it shows how a designer wants to edit a design in later stages through Boolean operations and allow to modify the particular part where designer wants to modify the part and not the complete body. For product benchmarking where few parameters are changing, changing the particular body can be a timesaver.