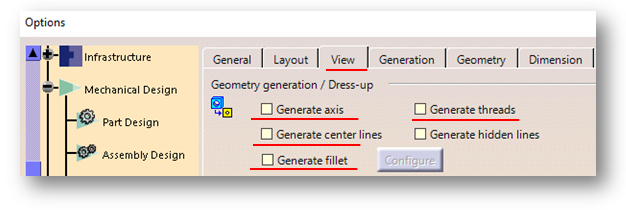
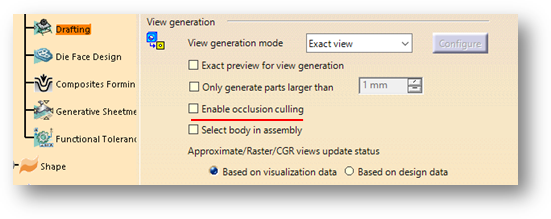
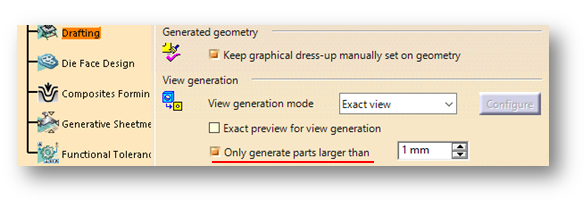
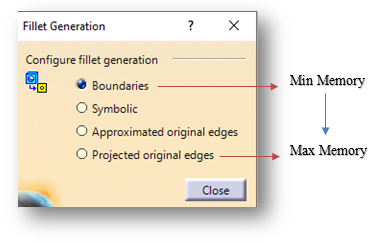
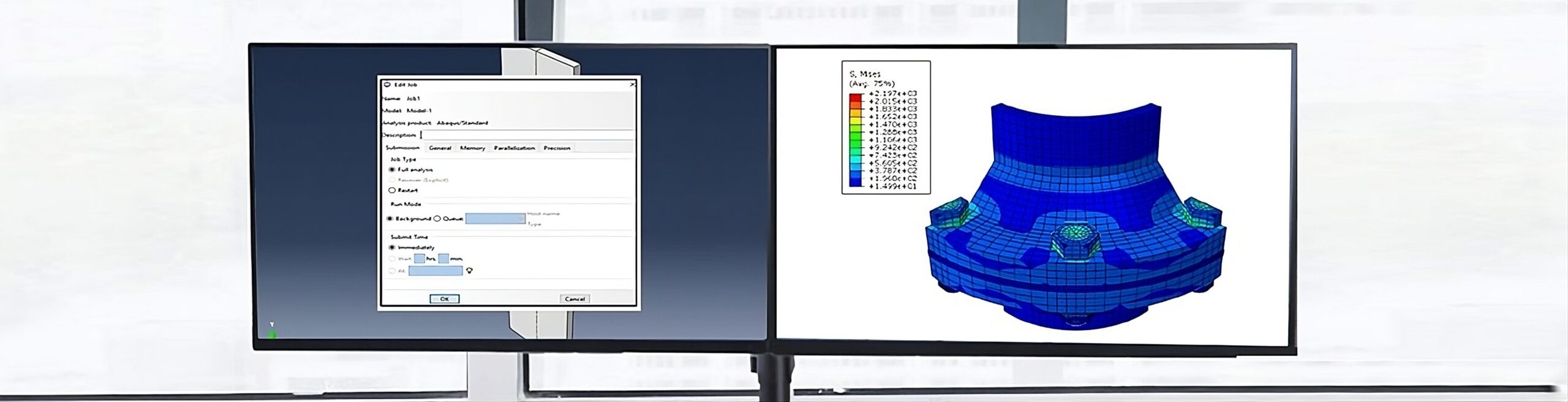
Working with large assemblies in the CATIA V5 system can be very demanding. Even with the use of extremely powerful machines and workstations, working with large assemblies often leads to the crashing of the system with the error message “Click OK to terminate” appearing. To avoid this error, this blog discusses some recommendations for optimizing the system to minimize the crashing of the program and to make it easy to work with large assembly sets.
- Cache System
System’s performance can be increased with the help of cache. When this option is activated, CATIA loads all parts of the set in visualization mode while not loading the whole history of the part. This helps in reducing the load on computer/system memory.To activate Cache System, click on Tools ➜ Options ➜ Infrastructure ➜ Product Structure ➜ under Cache Management tab, click “Work with the cache system.”
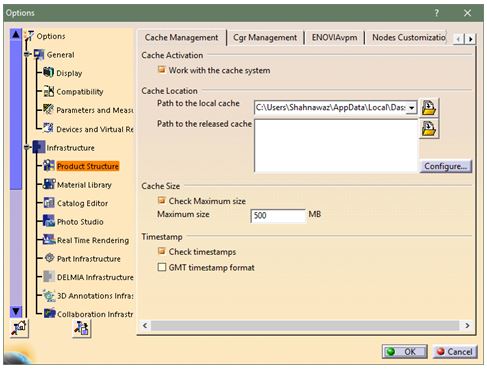
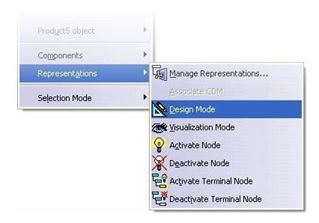
After restarting the program, CATIA will reload parts in visualization mode. If the part needs to be edited, switch to Design Mode which can be done by right clicking the part and selecting Representations and Design Mode.
- CGR Management
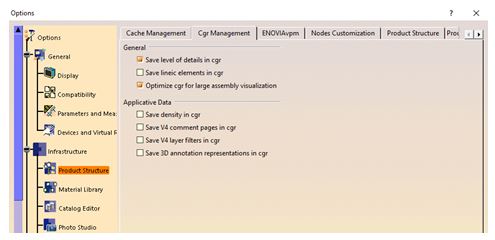
For large assemblies, CGR formats can be optimized. To optimize CGR formats, click on Tools ➜ Options ➜ Infrastructure ➜ Product Structure ➜ CGR Management tab.
- Display Option
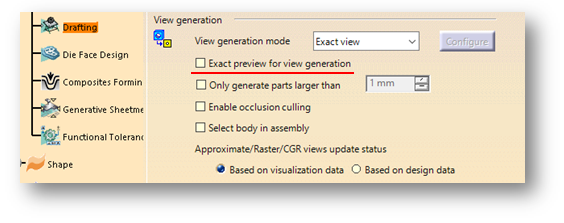
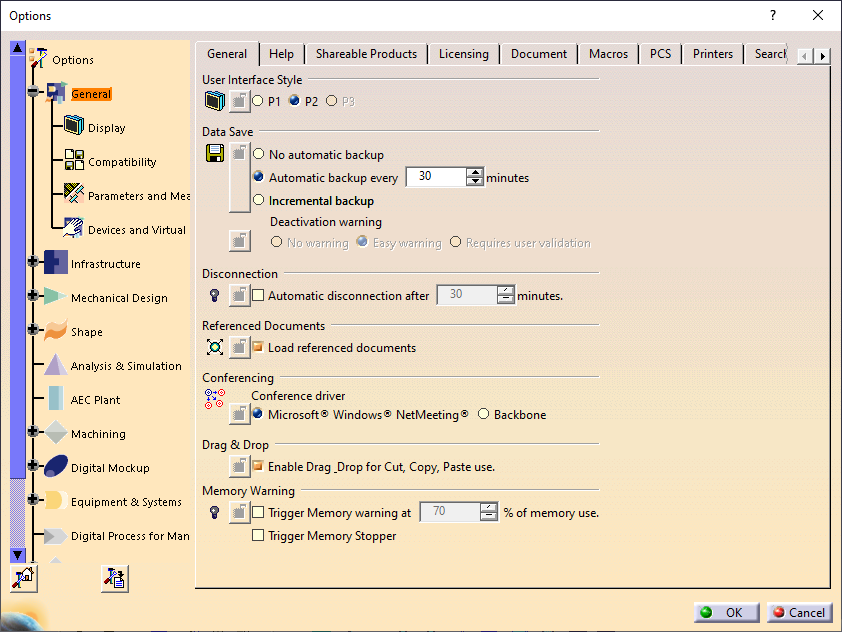
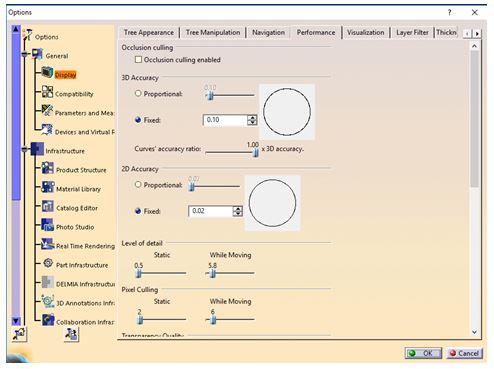
The changes in display options can be made in Performance Settings tab which will improve the results.Click on Tools ➜ Options ➜ General ➜ Display ➜ Performance tab.
It is recommended to turn off Occlusion Culling and set 3D Accuracy to 0.1 (increase in value improves performance), increase Level of Detail while Moving (increasing the value improves performance), increase Pixel culling while Moving (increasing the value improves performance).
- Disable Automatic Saving
By default, data is saved every 30 minutes in CATIA. System usually slows down while saving. The automatic data saving can be turned off by clicking Tools ➜ Options ➜ General tab and turning on No automatic backup in the Data Save settings.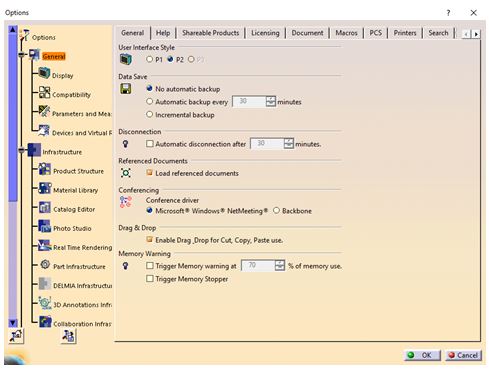
- Stack Size
The total number of “Undo” operations assigned to the CATIA session is the stack size. Reducing this number increases the memory capacity and thus the performance. Stack size can be changed by clicking on the PCS tab in the General menu.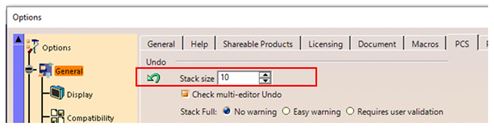
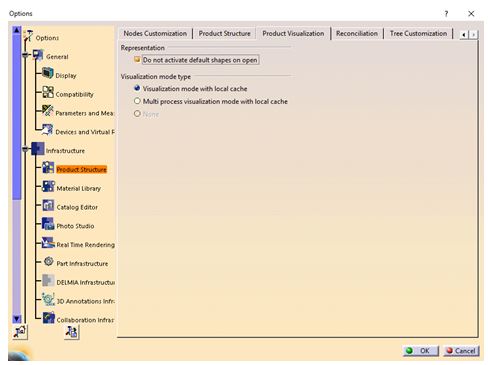
- Product Visualization Representation
The memory utilization will improve if sets are open in such a way that all components are deactivated and subsequently activated as needed. To change this setting, Do not activate default shapes on open option needs to be enabled within the Product Visualization (Tools ➜ Options ➜ Infrastructure ➜ Product Structure) menu.