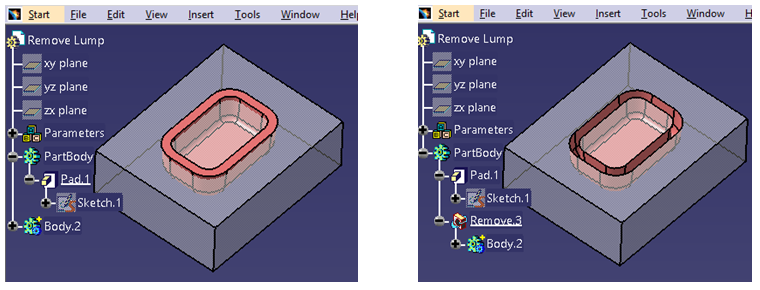
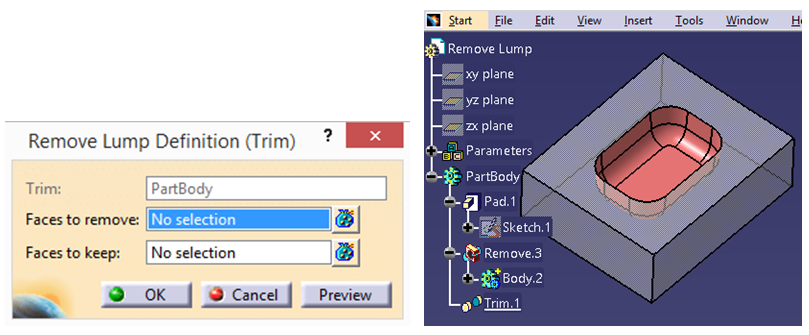
Every organization has its own standards and requirements when it comes to designing in CATIA. To adhere to these standards and requirements, some changes need to be made in the software application settings. In this article, setting up of global environment using customization setting from single source is explained in detail.
Introduction:
- From selecting license while opening CATIA V5 to modifying shortcut keys for commands, all settings done in CATIA are saved as CATSettings. CATSettings files are created once a user does some customization. A single CATSettings file may contain multiple attribute values.
- To make sure that users meet key company design practices and industry standards, CATSettings need to be administered. For the same reason, many OEMs create their own environment in CATIA and ask vendors to use the same.
- CATSettings created by users are stored in CATUserSettingPath.
- CATSettings created by administrators are stored in CATReferenceSettingPath in environment file.
There are many advantages of customizing CATIA settings which are listed below:
- It will lead to standardization of CAT Settings.
- Unnecessary start up settings and configurations are avoided.
- Default paths can be set which eliminates searching time.
- Custom Environment is created.
- Custom start parts and drafting standards are created.
- Best practices are followed by users.
The following steps are performed to set up CATIA V5 variables:
-
- Create a folder in the name of EDST_CATIA_Environment on network drive.
- Create two more folders in the name of say CAT_COLLECTION_STANDARD and CAT_Refrence_settings_path in EDST_CATIA_Environment folder.
- Click on CAT_Refrence_settings_path folder and copy the path from the Address
- Environment Editor can be opened by clicking Start > All Programs > CATIA > Tools > Environment Editor V5 R29 (the release issued from the user company).
- For setting new environment, click Environment ➜ New From and rename it as EDST_CATIA_Environment and click OK.
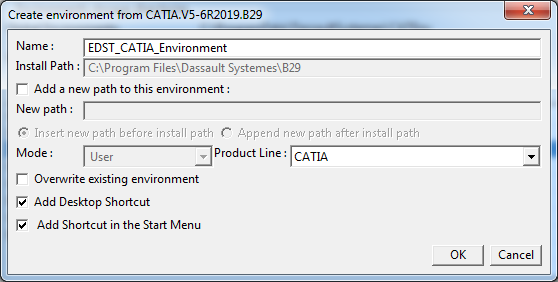
Environment is created and desktop icon is also generated for the same.
- The new environment file location is saved at the location:C:\User\hostname\AppData\Roaming\DassaultSystemes\CATEnv
- Select Environment (EDST_CATIA_Environment), click on CAT_Reference_settings_path and right click on variable.Click on Edit Variable. Now paste the path copied earlier.
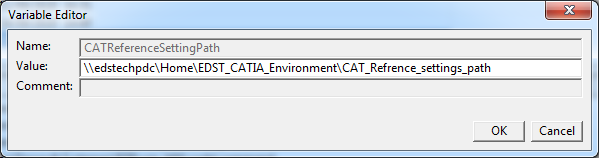
Similarly, copy and paste the same path for CAT_COLLECTION_STANDARD.
- Now save the modifications and exit the workbench.
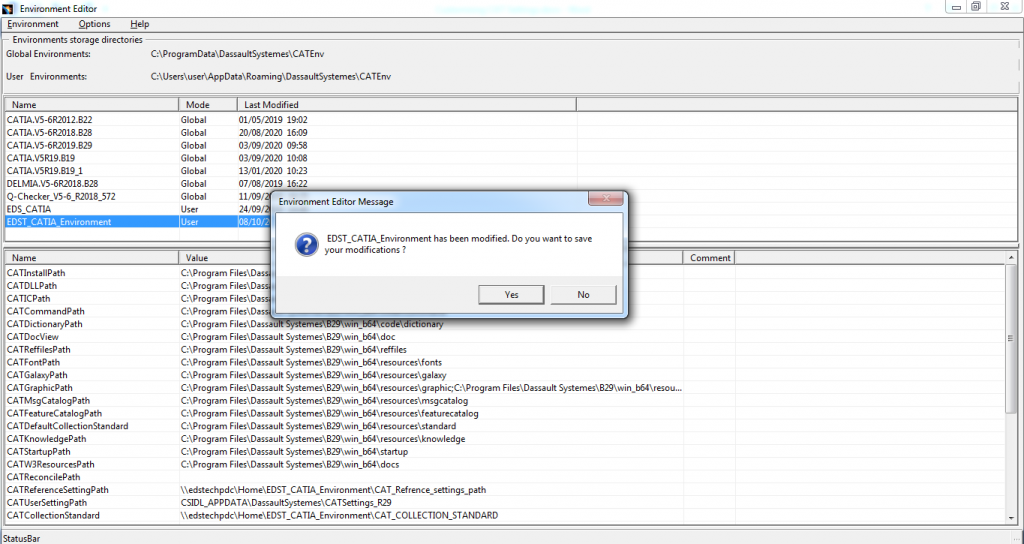
Now, the modified CATIA Environment is created successfully.
- Copy Environment file from C:\User\hostname\AppData\Roaming\DassaultSystemes\CATEnv and paste to the network drive. EDST_CATIA_Environment folder will be created.
The following are the steps to launch CATIA in Admin mode:
- Copy and paste the CATIA icon (in this document EDS_CATIA_Environment) on desktop.
- Rename EDS_CATIA_Environment to EDS_CATIA_Environment-ADMIN (only for reference)
- Right click on EDS_CATIA_Environment-ADMIN ➜ Properties
- Search for CNEXT in target tab and change exe to CNEXT–Admin.exe
- Change directory of Environment from “C:\Users\user\AppData\Roaming\DassaultSystemes\CATEnv“–nowindow to EDST_CATIA_Environment -direnv “Network Location“–nowindow for both EDS_CATIA_Environment and EDS_CATIA_Environment –ADMIN icons.
Changing CATIA environment paths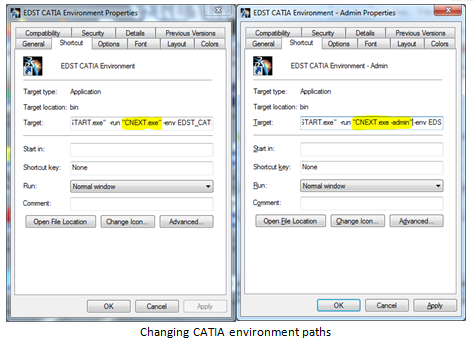
Now click EDS_CATIA_Environment-ADMIN and CATIA will be opened in Administration Mode.
Steps followed to modify System settings:
- Go to Tools ➜ Options
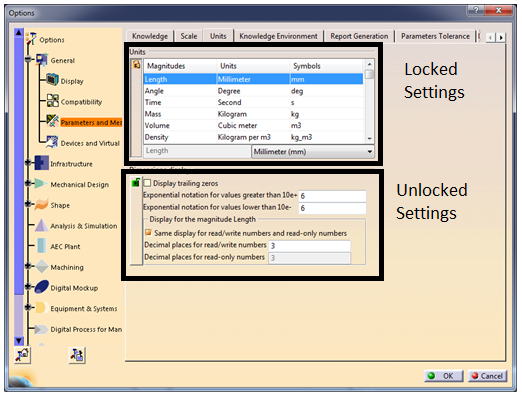
- Settings with a lock sign will appear
- Modify the required settings
- Click on the lock sign to lock the settings
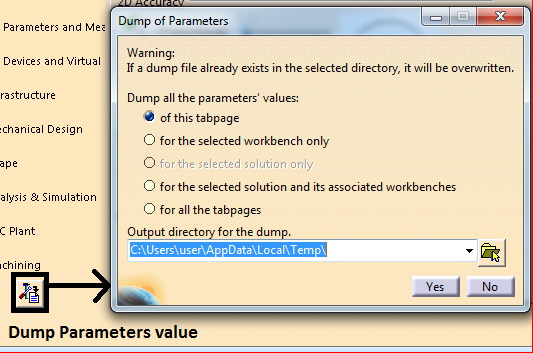
Reset and Dump settings:
- This is used to reset CATSettings to default value. User can reset the values which are changed to default. It can be changed for tab, workbench, selected solution and for all tab pages.
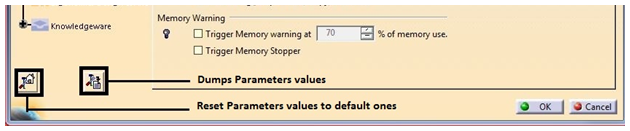
- To view values of given settings, comparing settings between different releases and viewing each attribute of settings in detail, dump settings are created. This setting is used to create CATVBS files of settings.